Service Store
This tutorial demonstrates the use of the Service Store feature.
Requirements
An installation of Legend with the following components:
- Studio
- Engine
- SDLC
Familiarity with the following Legend concepts:
- Data modeling with classes, associations
- Data modeling with stores, mappings, connections and runtimes
- Data modeling with Legend services
Showcase project
Service Store showcase project
Overview
In Legend, a Store is a "system" that stores data. A common store is a relational database like say Postgres.
But data is stored and served by other systems that are not databases. A ServiceStore treats a REST/HTTP based API (or "service") as a store of data.
This allows users to model and access data the same way irrespective of whether the data is from a relational database or a REST API.
With this definition in place, we can query a GraphQL server that implements the above types, as follows :
1. Basic modeling
We start with a simple model of Users and Repositories. This tutorial demonstrates how we map these logical concepts to the Github API.
// A user is associated with one/more repositories
Class legend::showcase::servicestore::models::Repository
{
id: Integer[1];
name: String[1];
full_name: String[1];
private: Boolean[1];
}
Class legend::showcase::servicestore::models::User
{
name: String[0..1];
email: String[0..1];
login: String[1];
id: Integer[1];
node_id: String[1];
avatar_url: String[1];
gravatar_id: String[1];
// elided ...
site_admin: Boolean[1];
starred_at: String[0..1];
}
Association legend::showcase::servicestore::models::UserRepository
{
user: legend::showcase::servicestore::models::User[0..1];
repositories: legend::showcase::servicestore::models::Repository[*];
}
2. Service Store
The ServiceStore DSL is how we describe the logical shape of an API or "service" that provides data.
###ServiceStore
ServiceStore legend::showcase::servicestore::store::GithubApis
(
Service UsersApi
(
path : '/users';
method : GET;
response : [legend::showcase::servicestore::models::User <- legend::showcase::servicestore::store::GithubApisBinding];
security : [];
)
ServiceGroup UserApiGroup
(
path : '/users';
Service UserApi
(
path : '/{username}';
method : GET;
parameters :
(
username : String ( location = path )
);
response : legend::showcase::servicestore::models::User <- legend::showcase::servicestore::store::GithubApisBinding;
security : [];
)
Service RepoApi
(
path : '/{username}/repos';
method : GET;
parameters :
(
username : String ( location = path )
);
response : legend::showcase::servicestore::models::Repository <- legend::showcase::servicestore::store::GithubApisBinding;
security : [];
)
)
)
In the example above, we declare a "service" called UserApi that is accessible over an HTTP path /users/{username} and returns data that can be mapped to the logical model class legend::showcase::servicestore::models::User
3. Binding
A binding is how we bind to an external data format. The Service definition points to a Binding.
Service UserApi
(
path : '/{username}';
method : GET;
parameters :
(
username : String ( location = path )
);
response : legend::showcase::servicestore::models::User <- legend::showcase::servicestore::store::GithubApisBinding;
security : [];
)
The definition of the binding declares that the "service" returns data of type JSON.
###ExternalFormat
Binding legend::showcase::servicestore::store::GithubApisBinding
{
contentType: 'application/json';
modelIncludes: [
legend::showcase::servicestore::models::User,
legend::showcase::servicestore::models::Repository
];
}
4. Mapping
Just as with other stores in Legend, the logical model is mapped to the logical definition of the store.
###Mapping
Mapping legend::showcase::servicestore::mapping::GithubAPIMapping
(
*legend::showcase::servicestore::models::User[user]: ServiceStore
{
~service [legend::showcase::servicestore::store::GithubApis] UsersApi
~service [legend::showcase::servicestore::store::GithubApis] UserApiGroup.UserApi
(
~request
(
parameters
(
username = $this.login
)
)
)
}
// elided ...
legend::showcase::servicestore::models::UserRepository: XStore
{
user[repo, user]: $that.login == $this.username,
repositories[user, repo]: $that.username == $this.login
}
)
In the example above, we map the logical class legend::showcase::servicestore::models::User to the data returned by the UsersApi.
We also map the class to the data returned by the UserApiGroup.UserApi. Since this service definition accepts a username parameter, we map the parameter as well.
TODO - Update the explanation of parameter mapping and also describe XStore
5. Connection
So far we have modeled a logical "service". Using the Connection we describe a specific physical service.
###Connection
ServiceStoreConnection legend::showcase::servicestore::connection::GithubConnection
{
store: legend::showcase::servicestore::store::GithubApis;
baseUrl: 'https://api.github.com';
}
In the above example, we declare that we want to consume data from the Github API hosted at https://api.github.com.
For production use cases, the Connection should include a definition of the authentication protocol to be used when connecting to the service.
6. Legend Service
Finally, we have a "Legend Service" that groups all the above concepts.
###Service
Service legend::showcase::servicestore::service::FetchGithubUsers
{
pattern: '/legend/showcase/servicestore/fetchUsers';
owners:
[
'hardik121998'
];
documentation: '';
autoActivateUpdates: true;
execution: Single
{
query: |legend::showcase::servicestore::models::User.all()->graphFetch(#{legend::showcase::servicestore::models::User{avatar_url,email,events_url,followers_url,following_url,gists_url,gravatar_id,html_url,id,login,name,node_id,organizations_url,received_events_url,repos_url,site_admin,starred_at,starred_url,subscriptions_url,type,url}}#)->serialize(#{legend::showcase::servicestore::models::User{avatar_url,email,events_url,followers_url,following_url,gists_url,gravatar_id,html_url,id,login,name,node_id,organizations_url,received_events_url,repos_url,site_admin,starred_at,starred_url,subscriptions_url,type,url}}#);
mapping: legend::showcase::servicestore::mapping::GithubAPIMapping;
runtime: legend::showcase::servicestore::runtime::ServiceStoreRuntime;
}
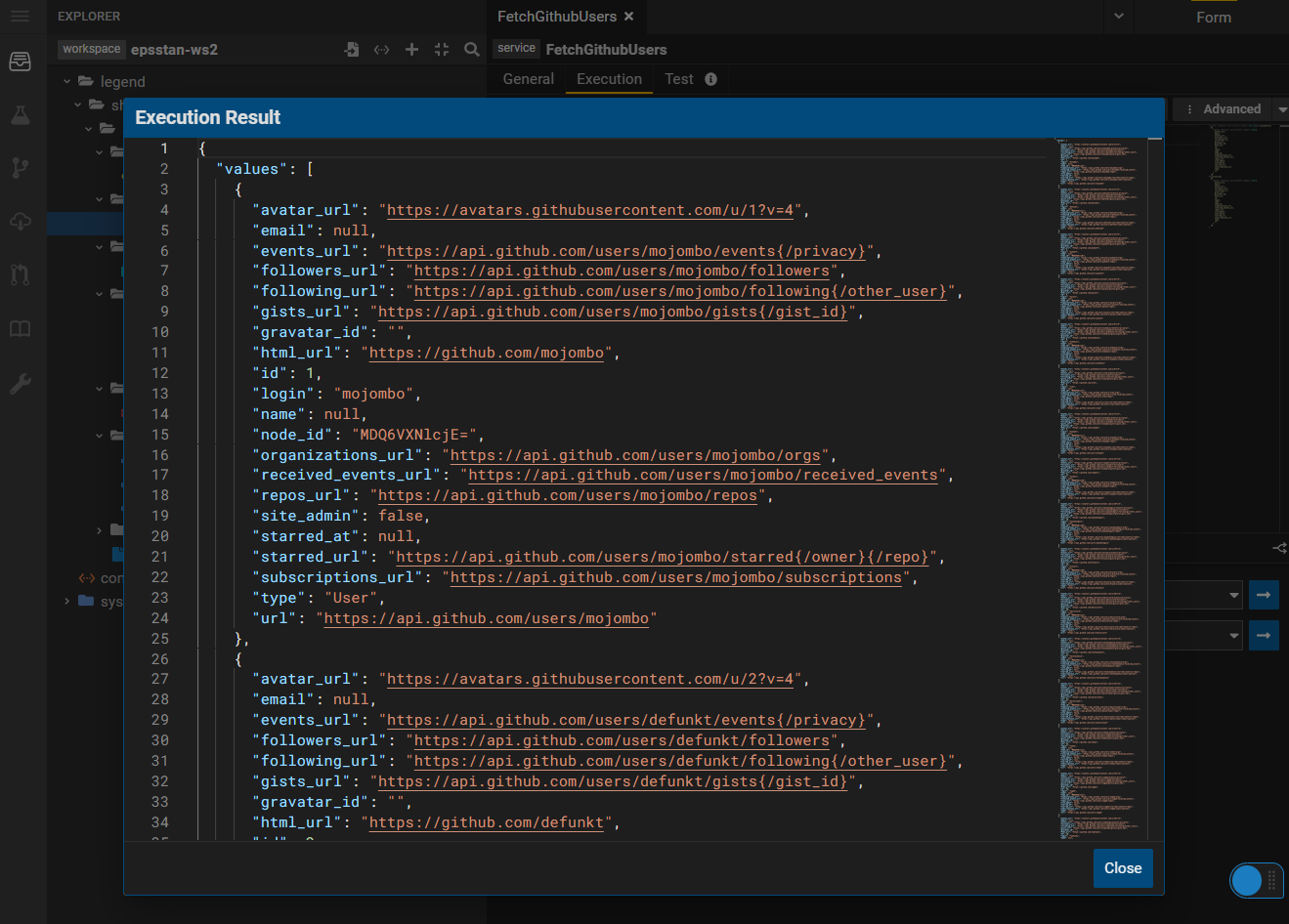
7. Execution
When the above service is executed, Legend connects to the Github API via the Connection, fetches the data and maps it to the logical domain classes.
Reference
Reference documentation on the design/implementation of the ServiceStore integration can be found here.
Code
Legend Engine source code is in the Maven modules named legend-engine-xt-servicestore-XXXX