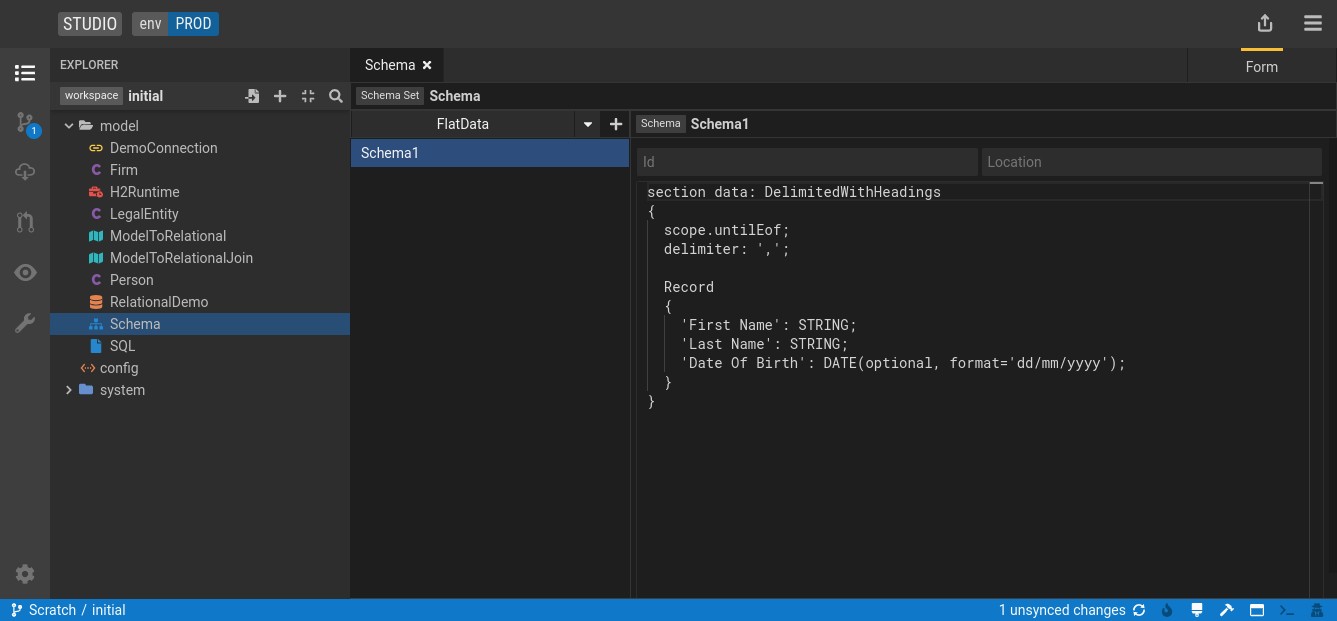
Create a Flat Data Schema
Create a Flat Data Schema
To create a Flat Data Schema
Click the + on the left-hand side and select New SchemaSet.
Enter a name for the SchemaSet
Ensure the type (top left) is selected as FlatData
Click the + next to the type to add a schema. For FlatData only a single schema should be added to a SchemaSet.
For FlatData the Id and Location can be left blank
Define the format of the file by entering the Flat Data Grammar
Flat Data Grammar
Sections
Each file format is defined by a schema (a single entry in a Legend SchemaSet). Each schema consists of one or more sections. A section is defined in grammar as:
section section_name: driver_type
{
properties
record_definition
}
The section_name provides a name for the section and must be unique within a schema.
The driver_type defines the type of data contained in the section. See below for details of the core driver types available.
The properties are specific to the driver type and are detailed below. Each property is specified either as a name or as a name and value. Each
property specified is terminated by a semicolon (;). See example below.
A record_definition may be given for driver types that support one.
Record definitions
A record definition is specified as:
Record
{
record_fields
}
Where a record_field is:
field_name: data_type(arguments)
or
field_name {address}: data_type(arguments)
dependent on whether the driver type is self-describing (without address) or not (with address).
The field_name is the field's name. For self-describing drivers this will be the name of the field exactly as it appears in the file (for example the heading of the
column). If the field_name contains non-alphanumeric characters (other than underscores) it should be enclosed in single quotes (''). For drivers that
are not self-describing the field_name can be any name that is unique within a record type. The address then specifies how the field is identified
within the data. The address is thus driver specific, it is always given within braces ({}).
Data Types
The valid data_types are given below. All data types can take arguments; when none are used the parentheses (()) are omitted. Arguments consist of
the single word optional or are a specified as argument=value. Multiple arguments are comma (,) separated.
STRING
Allowable Options:
optional
Examples:
STRINGSTRING(optional)
BOOLEAN
Allowable Options:
optionaltrueStringfalseString
Examples:
BOOLEANBOOLEAN(optional, trueString='Yes')BOOLEAN(trueString='Y',falseString='N')
Notes:
- If no
trueStringorfalseStringis specified thentrue(case insensitive) is taken to be true and any other value is considered false. - If only a
trueStringis specified then its value (case insensitive) is taken to be true and any other value is considered false. - If only a
falseStringis specified then its value (case insensitive) is taken to be false and any other value is considered true. - If both a
trueStringand afalseStringare specified their values (case insensitive) are taken to be true/false respectively and any other value is considered an error. - The properties
defaultTrueStringanddefaultFalseStringcan be used to specify behaviour for all BOOLEAN fields in a section.
INTEGER
Allowable Options:
optionalformat
Examples
INTEGERINTEGER(optional, format='#,##0')
Notes:
- Valid format strings are per Java's DecimalFormat (as used for integer-only strings).
- The format for all
INTEGERfields in a section can be specified using the defaultIntegerFormat property.
DECIMAL
Allowable Options:
optionalformat
Examples
DECIMALDECIMAL(optional, format='#,##0.0')
Notes:
- Valid format strings are per Java's DecimalFormat (as used for integer-only strings).
- The format for all
DECIMALfields in a section can be specified using the defaultDecimalFormat property.
DATE
Allowable Options:
optionalformat
Examples
DATEDATE(optional, format='dd/MM/yyyy')
Notes:
- Valid format strings are per Java's DateTimeFormatter (as used for date-only strings).
- The format for all
DATEfields in a section can be specified using thedefaultDateFormatproperty. - If a format is not specified, dates are expected to be in ISO 8601 format for dates only (
yyyy-MM-dd).
DATETIME
Allowable Options:
optionalformattimeZone
Examples
DATETIMEDATETIME(optional, format='dd/MM/yyyy HH:mm')DATETIME(timeZone='EST')
Notes:
- Valid format strings are per Java's DateTimeFormatter.
- The format for all
DATETIMEfields in a section can be specified using thedefaultDateTimeFormatproperty. - If a format is not specified, datetimes are expected to be in ISO 8601 format.
- If the datetime data does not include time zone information the time zone will be set according to the arguments/properties specified.
- Valid timeZone values are per Java's ZoneId including SHORT_IDS.
- The default time zone for all
DATETIMEfields in a section can be specified using thedefaultTimeZoneproperty. - When no time zone information is specified it is assumes to be UTC.
Driver: DelimitedWithHeadings
This driver reads data rows in which columns of data are separated by a delimiter. The first row specifies the headings for each column and hence defines the order of data. A classic CSV file is an example of this.
Properties
- Common Streaming Properties.
- Common Delimited Properties.
- Common Data Properties.
modelledColumnsMustBePresentoptional property which can be added as an option to assert that all fields specified in the Record must be present in the column headings row regardless of whether the field is optional.onlyModelledColumnsAllowedoptional property which can be added as an option to prohibit any fields not specified in the Record from being present in the column headings row.
Record
A Record definition is expected for this driver and its fields must not specify address values.
Driver: DelimitedWithoutHeadings
This driver reads data rows in which columns of data are separated by a delimiter and where no headings row is present.
Properties
Record
A Record definition is expected for this driver and its fields must specify address values.
The addresses are the one-based column positions of the data within the file.
Driver: ImmaterialLines
This driver is used to skip unnecessary lines of data.
Properties
Record
A Record definition must not be specified.
Common Delimited Properties
delimitermandatory property which specifies the column separator character(s).quoteCharoptional property which defines the character used for quoting strings within the file rows so that they can include delimiters and/or ends-of-lines.When quoting is used a quote character within a quoted string can be escaped by repeating it (for example the text 'It''s OK', where
quoteChar: '\'';has been specified, equates to the value It's OK).escapingCharoptional property which defines the character used to escape other characters. Escaping can be used both within and outside quoted text.Inside a quoted string the above example could have been
'It\'s OK', wherequoteChar: \'';andescapingChar: '\\'; have been specified, also equates to the value It's OK.Outside it can be used to escape delimiters such that the text
Hello\, World, Goodbye, wheredelimiter: ',';andescapingChar: '\\';have been specified, equates to two column values ofHello, WorldandGoodbye.nullString- optional property defining the text which equates to a null (missing) value. When this property is not specified the value is considered to be always present thus two delimiters in succession is interpreted as an empty string. To treat that as a null value you need to specifynullString: '';.Multiple
nullStringproperties can be used to specify more that one value.
Common Streaming Properties
recordSeparatoroptional property that defines the character(s) used to separate records within the file. This is commonly the end-of-line character(s).If this option is not specified the file will be separated using any of the commonly used line endings (
\n,\r\nand\r); this is usually the best option to alleviate issues with data being copied between different computers with different operating systems.mayContainBlankLinesoptional property which can be added as an option to specify that blank lines within the file should be ignored.scoperequired property that specifies the scope of the section. Options are:scope.default;use this unless you want a specific alternativescope.forNumberOfLines = n;if the section spans an exact number of linesscope.untilLineEquals = 'END';if the section spans until a marker line of the specified textscope.untilEof;if the section spans for the remainder of the data
Common Data Properties
defaultIntegerFormatdefaultDecimalFormatdefaultTrueStringdefaultFalseStringdefaultDateFormatdefaultDateTimeFormatdefaultTimeZone
See Data Types for usage.
Examples
This example defines a CSV file with:
- an ignored header row
- a column headings row
- data rows
section header: ImmaterialLines
{
scope.forNumberOfLines: 1;
}
section data: DelimitedWithHeadings
{
scope.default;
delimiter: ',';
modelledColumnsMustBePresent;
onlyModelledColumnsAllowed;
Record
{
'First Name': STRING;
'Last Name': STRING;
Age: INTEGER(optional);
}
}
This example defines a pipe-delimited file without headers. Columns are therefore addressed positionally:
section data: DelimitedWithoutHeadings
{
scope.default;
delimiter: '|';
Record
{
FirstName {1}: STRING;
LastName {2}: STRING;
Age {3}: INTEGER(optional);
}
}